First day with my shiny new iPhone, unlocked to work on Vodafone’s network – so far so good, pretty much loving it. Until I looked at the Bluetooth specs. Basically, this thing is only useful for mono headsets and carkits, and that’s it.
The iPhone has been certified under Bluetooth 2.0 + EDR, as can be seen in the BQB documents, but the PICS detail only handset and audio gateway profiles, with required signaling profiles such as RFCOMM, pretty much the bare minimum for a working Bluetooth hands-free system. What about the ton of other profiles, for example, A2DP, FTP, DUN…? Not included. The iPhone uses a CSR BlueCore4 Audioflash, which has 6MB of onboard FLASH memory, and could be upgraded provided that there is a host controller with access to the SPI port on the BC4. It seems that the iPhone uses Open Interface’s BLUEmagic 3.0 stack [PDF], which would imply an external host controller.
Now I’m starting to get confused – you usually choose a FLASH BlueCore if you intend to run software on it, be it CSR’s own stack, or a customized version of it. If you intend to use a host-based system, where the stack is handled by an external processor, you can buy way cheaper BlueCore ROM chips – and we’re talking between $1 and $3 a piece in savings. This may not seem much, but when multiplied it by Apple’s sales, you have a hefty sum. Below is a graphic that illustrates the differences between a host-based HCI system (left) and a standalone or ROM implementation (right):
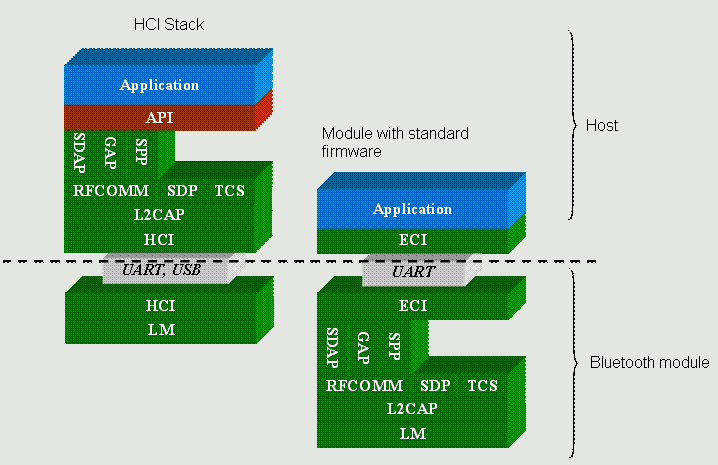
The big question still is – why is Apple so Bluetooth-unfriendly? Did they have certification problems and rushed through the bare minimum specs to claim Bluetooth compatibility? This seems strange as the iPhone was certified by CETECOM, which probably is the most experienced lab on Bluetooth certification in the world. Same applies to MacBooks and Mac Pros, they feature a few more profiles like FTP, but not A2DP. Hoping for a firmware update to fix this mess, over and out.